0/1 Knapsack
核心概念
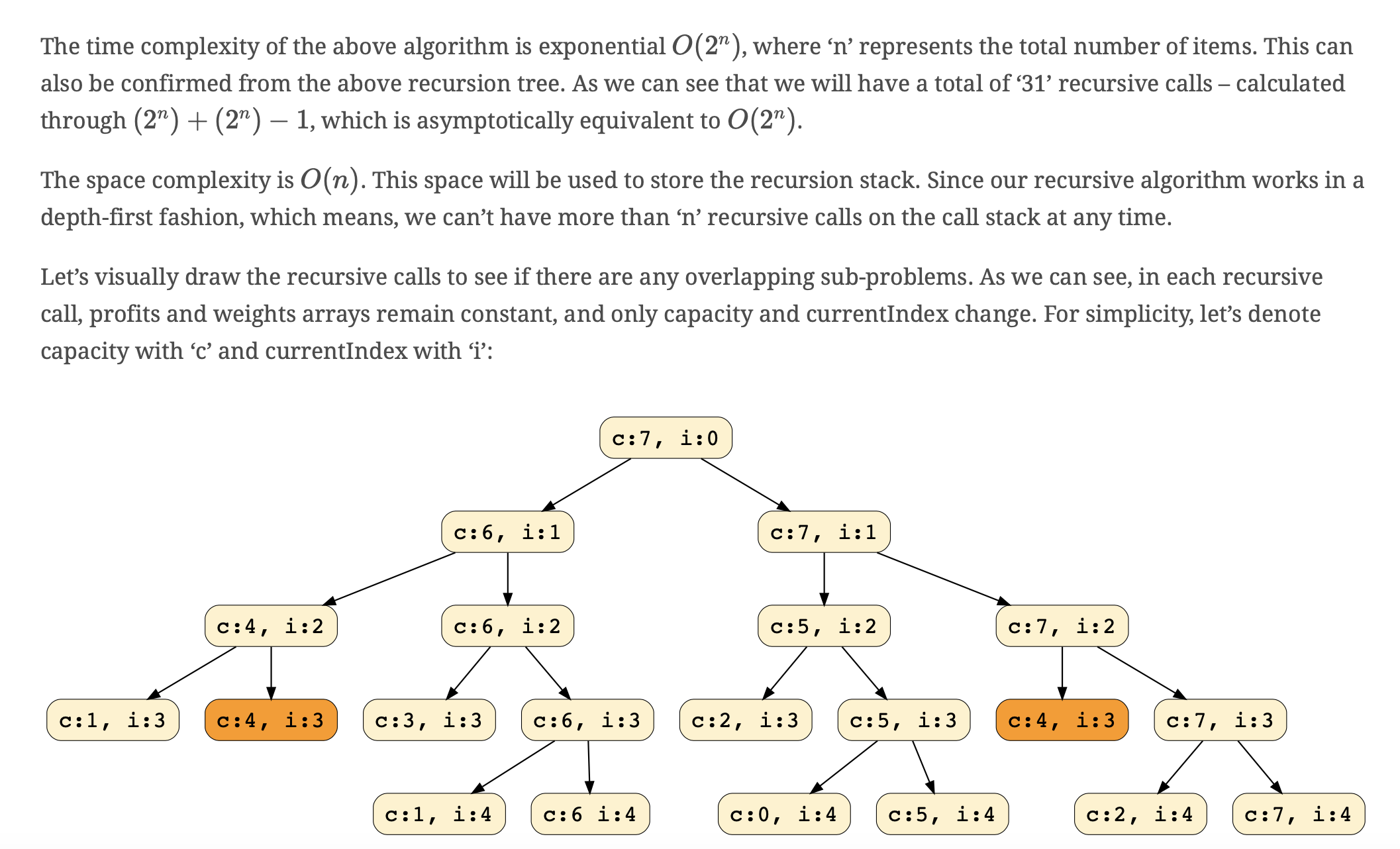
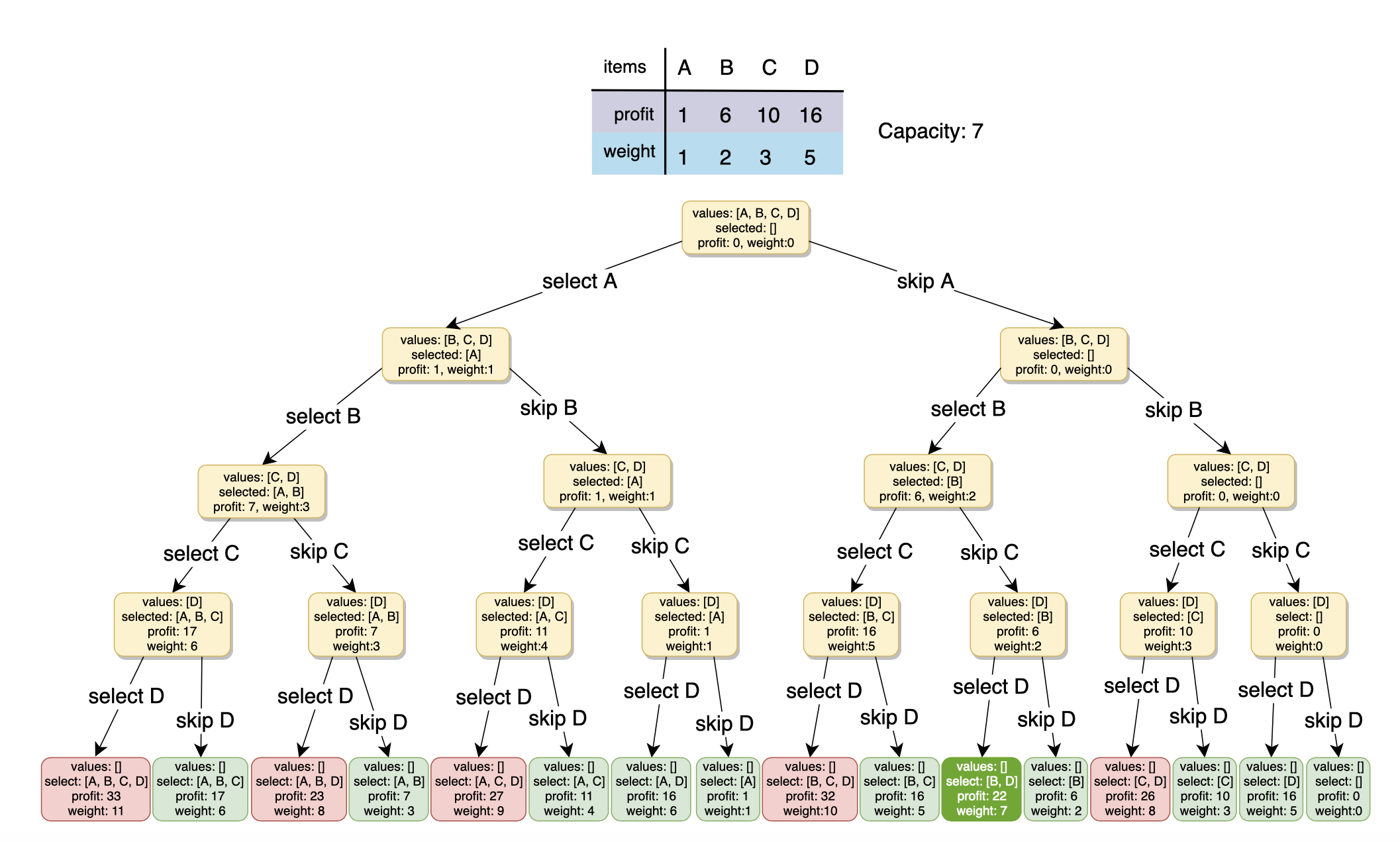
每遇到一個 item,都有要選 or 不要選這兩個分支,以此來寫出 recurrence formula。
簡介
暴力法的程式碼如下:
using namespace std;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
class Knapsack {
public:
int solveKnapsack(const vector<int> &profits, const vector<int> &weights, int capacity) {
return this->knapsackRecursive(profits, weights, capacity, 0);
}
private:
int knapsackRecursive(const vector<int> &profits, const vector<int> &weights, int capacity,
int currentIndex) {
// base checks
if (capacity <= 0 || currentIndex >= profits.size()) {
return 0;
}
// recursive call after choosing the element at the currentIndex
// if the weight of the element at currentIndex exceeds the capacity, we shouldn't process this
int profit1 = 0;
if (weights[currentIndex] <= capacity) {
profit1 =
profits[currentIndex] +
knapsackRecursive(profits, weights, capacity - weights[currentIndex], currentIndex + 1);
}
// recursive call after excluding the element at the currentIndex
int profit2 = knapsackRecursive(profits, weights, capacity, currentIndex + 1);
return max(profit1, profit2);
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
Knapsack ks;
vector<int> profits = {1, 6, 10, 16};
vector<int> weights = {1, 2, 3, 5};
int maxProfit = ks.solveKnapsack(profits, weights, 7);
cout << "Total knapsack profit ---> " << maxProfit << endl;
maxProfit = ks.solveKnapsack(profits, weights, 6);
cout << "Total knapsack profit ---> " << maxProfit << endl;
}Recursion + Memoization 的程式碼:
using namespace std;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
class Knapsack {
public:
int solveKnapsack(const vector<int> &profits, const vector<int> &weights, int capacity) {
vector<vector<int>> dp(profits.size(), vector<int>(capacity + 1, -1));
return this->knapsackRecursive(dp, profits, weights, capacity, 0);
}
private:
int knapsackRecursive(vector<vector<int>> &dp, const vector<int> &profits,
const vector<int> &weights, int capacity, int currentIndex) {
// base checks
if (capacity <= 0 || currentIndex >= profits.size()) {
return 0;
}
// if we have already solved a similar problem, return the result from memory
if (dp[currentIndex][capacity] != -1) {
return dp[currentIndex][capacity];
}
// recursive call after choosing the element at the currentIndex
// if the weight of the element at currentIndex exceeds the capacity, we shouldn't process this
int profit1 = 0;
if (weights[currentIndex] <= capacity) {
profit1 = profits[currentIndex] + knapsackRecursive(dp, profits, weights,
capacity - weights[currentIndex],
currentIndex + 1);
}
// recursive call after excluding the element at the currentIndex
int profit2 = knapsackRecursive(dp, profits, weights, capacity, currentIndex + 1);
dp[currentIndex][capacity] = max(profit1, profit2);
return dp[currentIndex][capacity];
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
Knapsack ks;
vector<int> profits = {1, 6, 10, 16};
vector<int> weights = {1, 2, 3, 5};
int maxProfit = ks.solveKnapsack(profits, weights, 7);
cout << "Total knapsack profit ---> " << maxProfit << endl;
maxProfit = ks.solveKnapsack(profits, weights, 6);
cout << "Total knapsack profit ---> " << maxProfit << endl;
}DP 解法的程式碼如下:
using namespace std;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
class Knapsack {
public:
int solveKnapsack(const vector<int> &profits, const vector<int> &weights, int capacity) {
// basic checks
if (capacity <= 0 || profits.empty() || weights.size() != profits.size()) {
return 0;
}
int n = profits.size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int>(capacity + 1));
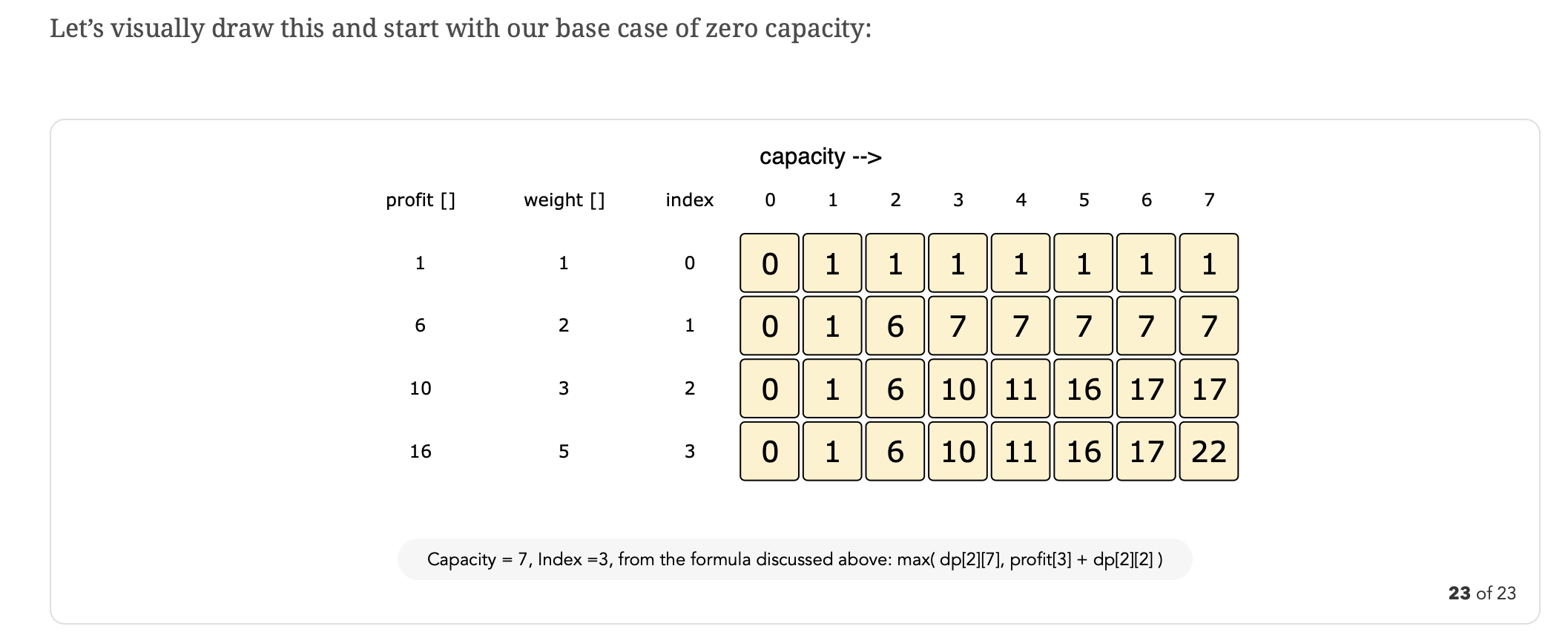
// populate the capacity=0 columns, with '0' capacity we have '0' profit
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dp[i][0] = 0;
}
// if we have only one weight, we will take it if it is not more than the capacity
for (int c = 0; c <= capacity; c++) {
if (weights[0] <= c) {
dp[0][c] = profits[0];
}
}
// process all sub-arrays for all the capacities
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (int c = 1; c <= capacity; c++) {
int profit1 = 0, profit2 = 0;
// include the item, if it is not more than the capacity
if (weights[i] <= c) {
profit1 = profits[i] + dp[i - 1][c - weights[i]];
}
// exclude the item
profit2 = dp[i - 1][c];
// take maximum
dp[i][c] = max(profit1, profit2);
}
}
// maximum profit will be at the bottom-right corner.
return dp[n - 1][capacity];
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
Knapsack ks;
vector<int> profits = {1, 6, 10, 16};
vector<int> weights = {1, 2, 3, 5};
int maxProfit = ks.solveKnapsack(profits, weights, 6);
cout << "Total knapsack profit ---> " << maxProfit << endl;
maxProfit = ks.solveKnapsack(profits, weights, 7);
cout << "Total knapsack profit ---> " << maxProfit << endl;
}這題的 DP 甚至可以繼續優化到只用 O(C) space 就解決,比如只用兩個 row:
using namespace std;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
// space optimization
class Knapsack {
public:
int solveKnapsack(const vector<int> &profits, const vector<int> &weights, int capacity) {
vector<vector<int>> dp(2, vector<int>(capacity+1, -1));
dp[0][0] = 0;
dp[1][0] = 0;
// Init first item row
for(int c=0; c<=capacity; c++) {
if (weights[0] <= c) {
dp[0][c] = profits[0];
}
}
// process all sub-arrays for all the capacities
for (int i = 1; i < profits.size(); i++) {
for (int c = 1; c <= capacity; c++) {
int profit1 = 0, profit2 = 0;
// include the item, if it is not more than the capacity
if (weights[i] <= c) {
profit1 = profits[i] + dp[(i - 1)%2][c - weights[i]];
}
// exclude the item
profit2 = dp[(i - 1)%2][c];
// take maximum
dp[i%2][c] = max(profit1, profit2);
}
}
return dp[1][capacity];
}
};或只用一個 row:
using namespace std;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
class Knapsack {
public:
int solveKnapsack(const vector<int> &profits, vector<int> &weights, int capacity) {
vector<int> dp(capacity+1, -1);
dp[0] = 0;
// Init dp array
for(int c=0; c<=capacity; c++) {
if (weights[0] <= c) {
dp[c] = profits[0];
}
}
// process all sub-arrays for all the capacities
for (int i = 1; i < profits.size(); i++) {
for (int c = capacity; c >= 0; c--) {
int profit1 = 0, profit2 = 0;
// include the item, if it is not more than the capacity
if (weights[i] <= c) {
profit1 = profits[i] + dp[c - weights[i]];
}
// exclude the item
profit2 = dp[c];
// take maximum
dp[c] = max(profit1, profit2);
}
}
return dp[capacity];
}
};Last updated